Protein digestibility kinetics: A key criterion for discriminating protein sources in feeds.
Proteins are biological macromolecules made up of amino acids. Protein bioavailability is strongly related to its amino acid composition, size, and mass range. Big proteins, protein-associated molecules and nucleic acids have lower digestibility than free amino acids and small peptides, which have been exposed to multiple nitrogen hydrolysis processes that make them more bioavailable (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Enzymatic protein digestion process
The kinetics of protein absorption should be considered in addition to protein digestibility. It allows nutritionists to properly assess the quality of the protein source.
Many properties and functionalities of proteins are related to their absorption kinetics. The kinetics of protein absorption helps categorize the protein fraction according to its speed of absorption. Four categories can be defined as flash, fast, slow and resistant along the digestive tract (Figure 2).
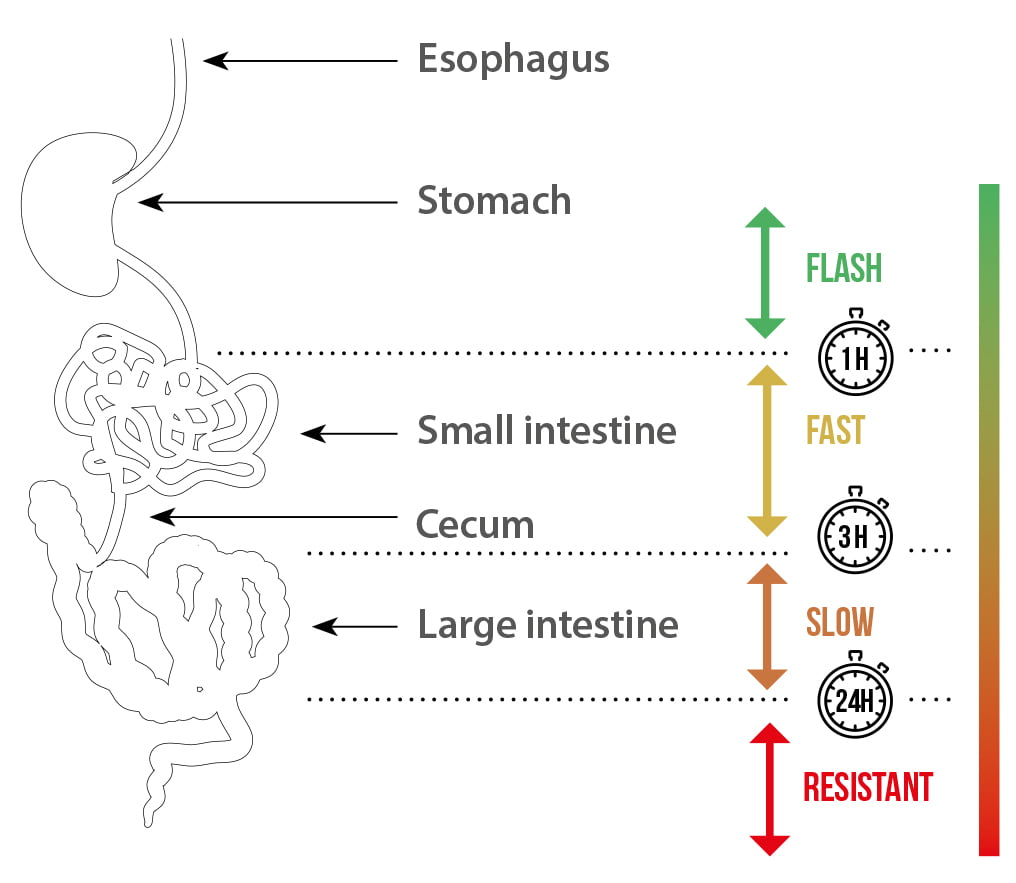
Figure 2. Kinetics of protein absorption: key parameters for protein functionalities
Hydrolyzed yeasts are a source of highly digestible and quickly absorbed proteins.
YELA PROSECURE is a specifically designed hydrolyzed yeast that offers highly digestible and functional nutrients supporting animal performance, digestive health and feed palatability while contributing to the feed-protein balance.





